Chapter : 3. Chemical Reactions
Triple covalent bond
Triple covalent bond :
A triple covalent bond is formed when three pairs of electrons (six electrons) are shared between the two combining atoms. A triple bond is shown by marking three short lines between the two symbols of the atoms.
EXAMPLES :
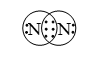
1. Formation of a nitrogen molecule (N2) :
An atom of nitrogen has five electrons in its valence shell. It requires three more electrons to attain the stable octet. This is achieved when two nitrogen atoms combine together by sharing three electrons each to form a nitrogen molecule.

Pictorially, a nitrogen molecule can be represented as in figure
Formation of an acetylene molecule (C2H2) :
In an acetylene molecule, two C atoms combine with two H atoms. Each C atom shares three of its valence electrons with the other C atom. One electron of each C atom is shared with one electron of a H atom.
Thus, in a molecule of acetylene, there is a triple covalent bond between the two C atoms and each C atom is joined to one H atom by a single covalent bond. Pictorially, a molecule of acetylene may be represented as in figure.

Characteristics of covalent compounds :
1. Covalent compounds are made up of neutral molecules. Hence, the forces of attraction between the molecules are weaker than those found in ionic compounds. Therefore, covalent compounds are usually volatile liquids or gases.
2. The melting and the boiling points of covalent compounds are generally low. Since covalent compounds are made up of neutral molecules, the forces of attraction between the molecules are very weak. So, a comparatively small amount of heat energy is required to break these weak intermolecular forces of attraction. Hence, they have low melting and boiling points.
3. Covalent compounds are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents.
4. Covalent compounds do not conduct electricity. This is because they are made up of neutral molecules, not ions, and do not produce ions in the molten state or in aqueous solutions.
A triple covalent bond is formed when three pairs of electrons (six electrons) are shared between the two combining atoms. A triple bond is shown by marking three short lines between the two symbols of the atoms.
EXAMPLES :
1. Formation of a nitrogen molecule (N2) :
An atom of nitrogen has five electrons in its valence shell. It requires three more electrons to attain the stable octet. This is achieved when two nitrogen atoms combine together by sharing three electrons each to form a nitrogen molecule.

Pictorially, a nitrogen molecule can be represented as in figure

Formation of an acetylene molecule (C2H2) :
In an acetylene molecule, two C atoms combine with two H atoms. Each C atom shares three of its valence electrons with the other C atom. One electron of each C atom is shared with one electron of a H atom.
Thus, in a molecule of acetylene, there is a triple covalent bond between the two C atoms and each C atom is joined to one H atom by a single covalent bond. Pictorially, a molecule of acetylene may be represented as in figure.

Characteristics of covalent compounds :
1. Covalent compounds are made up of neutral molecules. Hence, the forces of attraction between the molecules are weaker than those found in ionic compounds. Therefore, covalent compounds are usually volatile liquids or gases.
2. The melting and the boiling points of covalent compounds are generally low. Since covalent compounds are made up of neutral molecules, the forces of attraction between the molecules are very weak. So, a comparatively small amount of heat energy is required to break these weak intermolecular forces of attraction. Hence, they have low melting and boiling points.
3. Covalent compounds are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents.
4. Covalent compounds do not conduct electricity. This is because they are made up of neutral molecules, not ions, and do not produce ions in the molten state or in aqueous solutions.
Trending Articles & Blogs
- Physics Tutor, Math Tutor Improve Your Child’s Knowledge
- How to Get Maximum Marks in Examination Preparation Strategy by Dr. Mukesh Shrimali
- 5 Important Tips To Personal Development Apply In Your Daily Life
- Breaking the Barriers Between High School and Higher Education
- 14 Vocational courses after class 12th
- Tips to Get Maximum Marks in Physics Examination
- Get Full Marks in Biology Class 12 CBSE
Download Old Sample Papers For Class X & XII
Download Practical Solutions of Chemistry and Physics for Class 12 with Solutions
Recent Questions Asked
- Newton’s laws of motion asked by Dr. Mukesh Shrimali
- Process of nutrition in Amoeba asked by Rajiv Sharma
- Importance of studying physics subject in school after 10th asked by Rajiv
- Refraction Through Prism in Different Medium asked by Kirti Sharma
- Ratio and Proportion Question asked by Education Desk
- Explain all the 12 tenses with example asked by Qwerty
- Refraction Through Prism in Different Medium asked by Seema Shrimali