Chapter : 3. Atoms & Molecules
Molecular mass/Formula mass
Molecular mass expresses as to how many times a molecule of a substance is heavier than 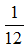 th of the mass of an atom of carbon (carbon-12). Thus,
th of the mass of an atom of carbon (carbon-12). Thus,
Molecular mass =
Molecular mass = 2 × vapour density
Example A molecule of water is 18 times heavier than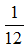 th of the mass of carbon atom. Therefore, the molecular mass of water is 18 u.
th of the mass of carbon atom. Therefore, the molecular mass of water is 18 u.
Calculation of molecular mass from atomic masses
The molecules are made up of two or more atoms of different elements. Therefore, the molecular mass may be calculated as the sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms in a molecule of that substance.
Example. Ammonia has the formula, NH3. It consists of one atom of N and three atoms of H. The atomic mass of N and H are 14.0 and 1 respectively. Therefore, the molecular mass of NH3 is
Molecular mass of NH3 = At. mass of N + 3 × At. mass of H
= 14 + 3 × 1 = 17 u
Example. Sulphuric acid has the formula H2SO4. It consists of two H, one S and four O atoms. The atomic masses of H, S and O are 1,32 and 16 respectively. Therefore, the molecular mass of H2SO4 is
Molecular mass of H2SO4 =
(2 × at. m. of H) + (1 × at. m. of S)
+ (4 × at. m. of O)
= (2 × 1) + (1 × 32) + (4 × 16) = 98 u
Gram molecular mass
The molecular mass of a substance expressed in gram is called its gram molecular mass.
Example. Molecular mass of oxygen, O2 = 32 u
So, gram molecular mass of oxygen, O2 = 32 grams.
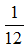 th of the mass of an atom of carbon (carbon-12). Thus,
th of the mass of an atom of carbon (carbon-12). Thus, Molecular mass =

Molecular mass = 2 × vapour density
Example A molecule of water is 18 times heavier than
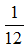 th of the mass of carbon atom. Therefore, the molecular mass of water is 18 u.
th of the mass of carbon atom. Therefore, the molecular mass of water is 18 u. Calculation of molecular mass from atomic masses
The molecules are made up of two or more atoms of different elements. Therefore, the molecular mass may be calculated as the sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms in a molecule of that substance.
Example. Ammonia has the formula, NH3. It consists of one atom of N and three atoms of H. The atomic mass of N and H are 14.0 and 1 respectively. Therefore, the molecular mass of NH3 is
Molecular mass of NH3 = At. mass of N + 3 × At. mass of H
= 14 + 3 × 1 = 17 u
Example. Sulphuric acid has the formula H2SO4. It consists of two H, one S and four O atoms. The atomic masses of H, S and O are 1,32 and 16 respectively. Therefore, the molecular mass of H2SO4 is
Molecular mass of H2SO4 =
(2 × at. m. of H) + (1 × at. m. of S)
+ (4 × at. m. of O)
= (2 × 1) + (1 × 32) + (4 × 16) = 98 u
Gram molecular mass
The molecular mass of a substance expressed in gram is called its gram molecular mass.
Example. Molecular mass of oxygen, O2 = 32 u
So, gram molecular mass of oxygen, O2 = 32 grams.
Trending Articles & Blogs
- Physics Tutor, Math Tutor Improve Your Child’s Knowledge
- How to Get Maximum Marks in Examination Preparation Strategy by Dr. Mukesh Shrimali
- 5 Important Tips To Personal Development Apply In Your Daily Life
- Breaking the Barriers Between High School and Higher Education
- 14 Vocational courses after class 12th
- Tips to Get Maximum Marks in Physics Examination
- Get Full Marks in Biology Class 12 CBSE
Download Old Sample Papers For Class X & XII
Download Practical Solutions of Chemistry and Physics for Class 12 with Solutions
Recent Questions Asked
- Newton’s laws of motion asked by Dr. Mukesh Shrimali
- Process of nutrition in Amoeba asked by Rajiv Sharma
- Importance of studying physics subject in school after 10th asked by Rajiv
- Refraction Through Prism in Different Medium asked by Kirti Sharma
- Ratio and Proportion Question asked by Education Desk
- Explain all the 12 tenses with example asked by Qwerty
- Refraction Through Prism in Different Medium asked by Seema Shrimali