Chapter : 6. Carbon and Its Compound
Chemical Properties of Carbon Compounds
Chemical Properties of Carbon Compounds
64. Combustion of Carbon: Carbon, in all allotropic forms, burns in presence of oxygen to form carbon dioxide with evolution of heat and light energy. In case of diamond, graphite and fullerene, they burn completely to form CO2 because they are purest form of carbon.
C + O2 → CO2 + Heat + light
Most of the carbon compounds are combustible and burn in presence of oxygen to form CO2 and H2O. e.g.,
CH4(g) + 2O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2H2O(l) + heat + light
2H2H6(g) + 7O2(g) → 4CO2(g) + 6H2O(l) + Heat + light
2CH3OH(g) + 3O2(g) → 2CO2(g) + 4H2O(l) + heat light
CH3CH2OH(l) + 3O2 → 2CO2(g) + 3H2O(l) + heat
CH3COOH (l) + 2O2(g) → 2CO2(g) + 2H2O(l) + heat
65. Combustion of Hydrocarbons : If hydrocarbons are burnt in limited supply of oxygen then smoky flame is produced due to incomplete combustion whereas in excess of oxygen, complete combustion takes place and non-luminous bluish flame with high temperature is produced.
66. Oxidising Agent : Those substances which can add oxygen to starting material are called oxidising agents, e.g., alkaline KMnO4 and acidified potassium dichromate
75. Combustion of Acetylene : Acetylene burns in presence of oxygen to form CO2 and H2O.
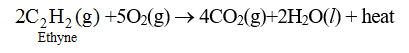
64. Combustion of Carbon: Carbon, in all allotropic forms, burns in presence of oxygen to form carbon dioxide with evolution of heat and light energy. In case of diamond, graphite and fullerene, they burn completely to form CO2 because they are purest form of carbon.
C + O2 → CO2 + Heat + light
Most of the carbon compounds are combustible and burn in presence of oxygen to form CO2 and H2O. e.g.,
CH4(g) + 2O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2H2O(l) + heat + light
2H2H6(g) + 7O2(g) → 4CO2(g) + 6H2O(l) + Heat + light
2CH3OH(g) + 3O2(g) → 2CO2(g) + 4H2O(l) + heat light
CH3CH2OH(l) + 3O2 → 2CO2(g) + 3H2O(l) + heat
CH3COOH (l) + 2O2(g) → 2CO2(g) + 2H2O(l) + heat
65. Combustion of Hydrocarbons : If hydrocarbons are burnt in limited supply of oxygen then smoky flame is produced due to incomplete combustion whereas in excess of oxygen, complete combustion takes place and non-luminous bluish flame with high temperature is produced.
66. Oxidising Agent : Those substances which can add oxygen to starting material are called oxidising agents, e.g., alkaline KMnO4 and acidified potassium dichromate
75. Combustion of Acetylene : Acetylene burns in presence of oxygen to form CO2 and H2O.
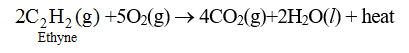
Trending Articles & Blogs
- Physics Tutor, Math Tutor Improve Your Child’s Knowledge
- How to Get Maximum Marks in Examination Preparation Strategy by Dr. Mukesh Shrimali
- 5 Important Tips To Personal Development Apply In Your Daily Life
- Breaking the Barriers Between High School and Higher Education
- 14 Vocational courses after class 12th
- Tips to Get Maximum Marks in Physics Examination
- Get Full Marks in Biology Class 12 CBSE
Download Old Sample Papers For Class X & XII
Download Practical Solutions of Chemistry and Physics for Class 12 with Solutions
Recent Questions Asked
- Newton’s laws of motion asked by Dr. Mukesh Shrimali
- Process of nutrition in Amoeba asked by Rajiv Sharma
- Importance of studying physics subject in school after 10th asked by Rajiv
- Refraction Through Prism in Different Medium asked by Kirti Sharma
- Ratio and Proportion Question asked by Education Desk
- Explain all the 12 tenses with example asked by Qwerty
- Refraction Through Prism in Different Medium asked by Seema Shrimali