Chapter : 3. Chemical Reactions
Balancing
Balancing :
The process of making atoms of various elements equal in an equation on either side is called balancing.
Steps in Balancing of Chemical Equations :
A number of steps are involved in balancing a chemical equation
Example 1 : Na + H2O → NaOH + H2
Step-1 : Examine the number of atoms of different elements present in unbalanced equations

Step-2 : Pick an element to balance the equation. In the above equation Na and O are balanced, Hydrogen is not.
Step 3 : To balance Hydrogen on both sides we need to multiply H2O by 2 which makes Hydrogen atoms equal to 4 on the reactants' side. To make Hydrogen 4 on the products' side, multiply NaOH by 2. Now oxygen has become 2 on both side. But Sodium atoms has become two on the products' side. Multiply Na by 2 on the reactants side so that they become equal on both side. The steps are as follows :
(i) Na + 2H2O → NaOH + H2
(ii) Na + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2
(iii) 2Na + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2
(iv) The equation is now balanced.
Example: Fe + H2O → Fe3O4 + H2
Step 1:

Step-2 : Pick up the compound which has the maximum number of atoms whether a reactant or a product, and in that compound select the elements which has the highest number of atoms, e.g., we select Fe3O4 in the above equation :
To balance oxygen atoms,

To equalise the number of atoms, we put the coefficient on the left side of the formula.
A coefficient is a small whole number, like coefficients used in algebraic equations.
You must keep in mind that we can put coefficients but we cannot change the subscripts in the formula, i.e., to balance Oxygen atoms, we can put the coefficient 4 as 4H2O and not H2O4 or (H2O)4 Now the partly balanced equation becomes as follows : -

Step 3: Pick up the second element to balance this partly balanced equation. Let us try to balance hydrogen atoms.
In partly balanced equation. Atoms of Hydrogen

To equalise the number of Hydrogen atoms, we use 4 as the coefficient of H2 in the products.
Fe(s) + 4H2O(g) → Fe3O4(s) + 4H2
Step 4: Pick up third element to be balanced. The element which is left to be balanced is Fe.।

To equalise, we use 3 as coefficient of Fe in reactants.
3Fe + 4H2O → Fe3O4 + 4H2
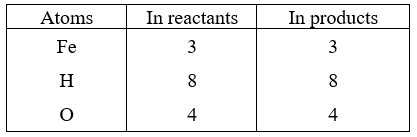
The equation is balanced because atoms of all the elements are equal on both sides.
This method of balancing equation is known as hit and trial method.
The process of making atoms of various elements equal in an equation on either side is called balancing.
Steps in Balancing of Chemical Equations :
A number of steps are involved in balancing a chemical equation
Example 1 : Na + H2O → NaOH + H2
Step-1 : Examine the number of atoms of different elements present in unbalanced equations

Step-2 : Pick an element to balance the equation. In the above equation Na and O are balanced, Hydrogen is not.
Step 3 : To balance Hydrogen on both sides we need to multiply H2O by 2 which makes Hydrogen atoms equal to 4 on the reactants' side. To make Hydrogen 4 on the products' side, multiply NaOH by 2. Now oxygen has become 2 on both side. But Sodium atoms has become two on the products' side. Multiply Na by 2 on the reactants side so that they become equal on both side. The steps are as follows :
(i) Na + 2H2O → NaOH + H2
(ii) Na + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2
(iii) 2Na + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2
(iv) The equation is now balanced.
Example: Fe + H2O → Fe3O4 + H2
Step 1:

Step-2 : Pick up the compound which has the maximum number of atoms whether a reactant or a product, and in that compound select the elements which has the highest number of atoms, e.g., we select Fe3O4 in the above equation :
To balance oxygen atoms,

To equalise the number of atoms, we put the coefficient on the left side of the formula.
A coefficient is a small whole number, like coefficients used in algebraic equations.
You must keep in mind that we can put coefficients but we cannot change the subscripts in the formula, i.e., to balance Oxygen atoms, we can put the coefficient 4 as 4H2O and not H2O4 or (H2O)4 Now the partly balanced equation becomes as follows : -

Step 3: Pick up the second element to balance this partly balanced equation. Let us try to balance hydrogen atoms.
In partly balanced equation. Atoms of Hydrogen

To equalise the number of Hydrogen atoms, we use 4 as the coefficient of H2 in the products.
Fe(s) + 4H2O(g) → Fe3O4(s) + 4H2
Step 4: Pick up third element to be balanced. The element which is left to be balanced is Fe.।

To equalise, we use 3 as coefficient of Fe in reactants.
3Fe + 4H2O → Fe3O4 + 4H2

The equation is balanced because atoms of all the elements are equal on both sides.
This method of balancing equation is known as hit and trial method.
Trending Articles & Blogs
- Physics Tutor, Math Tutor Improve Your Child’s Knowledge
- How to Get Maximum Marks in Examination Preparation Strategy by Dr. Mukesh Shrimali
- 5 Important Tips To Personal Development Apply In Your Daily Life
- Breaking the Barriers Between High School and Higher Education
- 14 Vocational courses after class 12th
- Tips to Get Maximum Marks in Physics Examination
- Get Full Marks in Biology Class 12 CBSE
Download Old Sample Papers For Class X & XII
Download Practical Solutions of Chemistry and Physics for Class 12 with Solutions
Recent Questions Asked
- Newton’s laws of motion asked by Dr. Mukesh Shrimali
- Process of nutrition in Amoeba asked by Rajiv Sharma
- Importance of studying physics subject in school after 10th asked by Rajiv
- Refraction Through Prism in Different Medium asked by Kirti Sharma
- Ratio and Proportion Question asked by Education Desk
- Explain all the 12 tenses with example asked by Qwerty
- Refraction Through Prism in Different Medium asked by Seema Shrimali