Chapter : 6. Carbon and Its Compound
Physical amd Chemical Properties of Ethanoic Aacid
84. Physical properties :
(i) Ethanoic acid is vinegar smelling liquid. The lower carboxylic acids are liquids whereas higher ones are solids.
(ii) Ethanoic acid is sour in taste. Other lower carboxylic acids are also sour in taste.
(iii) Ethanoic acid has boiling point 391 K. Carboxylic acids have higher boiling points than corresponding alcohols, aldehydes and ketones.
(iv) Acetic acid is soluble in water, i.e., it is miscible with water in all proportions. The lower carboxylic acids are soluble in water but solubility in water decreases with increase in molecular weight.
(v) Acetic acid freezes at 290 K. Thus, in cold weather crystallization of acetic acid may take place that is why pure acetic acid is called glacial acetic acid.
85. Chemical Properties :
(i) Ethanoic acid is weak acid but it turns blue litmus red.
(ii) Reaction with Metale. Ethanoic acid reacts with metals like Na, K, Zn etc. to form metal ethanoates and hydrogen gas.
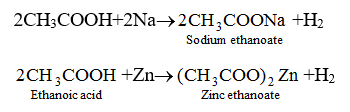
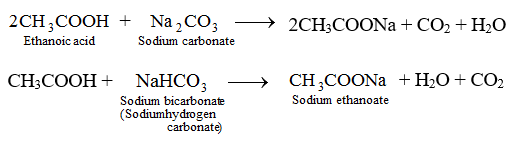
(iii) Reaction with Carbonates. Ethanoic acid reacts with bicarbonates and carbonates and produces brisk effervescence due to formation of carbon dioxide, CO2.
(iv) Reaction with Base. Ethanoic acid reacts with sodium hydroxide to form sodium ethanoate and water.

(v) Decarboxylation (Removal of CO2) When sodium salt of ethanoic acid, i.e., sodium ethanoate is heated with soda lime (3 parts of NaOH and 1 part of CaO), methane gas is formed.

This reaction is known as decarboxylation because a molecule of CO2 is removed from a molecule of acid.
(vi) Reaction with alcohols. Ethanoic acid reacts with ethanol in presence of concentrated sulphuric acid to form esters which are pleasant fruity smelling compounds.
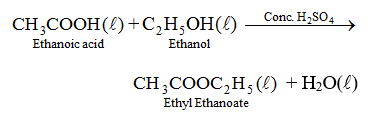
(vii) Reduction. Acetic acid, on reduction with lithium aluminium hydride, results in formation of ethanal, which on further reduction gives ethanol.

(i) Ethanoic acid is vinegar smelling liquid. The lower carboxylic acids are liquids whereas higher ones are solids.
(ii) Ethanoic acid is sour in taste. Other lower carboxylic acids are also sour in taste.
(iii) Ethanoic acid has boiling point 391 K. Carboxylic acids have higher boiling points than corresponding alcohols, aldehydes and ketones.
(iv) Acetic acid is soluble in water, i.e., it is miscible with water in all proportions. The lower carboxylic acids are soluble in water but solubility in water decreases with increase in molecular weight.
(v) Acetic acid freezes at 290 K. Thus, in cold weather crystallization of acetic acid may take place that is why pure acetic acid is called glacial acetic acid.
85. Chemical Properties :
(i) Ethanoic acid is weak acid but it turns blue litmus red.
(ii) Reaction with Metale. Ethanoic acid reacts with metals like Na, K, Zn etc. to form metal ethanoates and hydrogen gas.
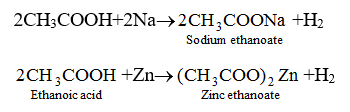
(iii) Reaction with Carbonates. Ethanoic acid reacts with bicarbonates and carbonates and produces brisk effervescence due to formation of carbon dioxide, CO2.

(iv) Reaction with Base. Ethanoic acid reacts with sodium hydroxide to form sodium ethanoate and water.

(v) Decarboxylation (Removal of CO2) When sodium salt of ethanoic acid, i.e., sodium ethanoate is heated with soda lime (3 parts of NaOH and 1 part of CaO), methane gas is formed.

This reaction is known as decarboxylation because a molecule of CO2 is removed from a molecule of acid.
(vi) Reaction with alcohols. Ethanoic acid reacts with ethanol in presence of concentrated sulphuric acid to form esters which are pleasant fruity smelling compounds.
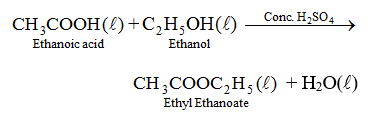
(vii) Reduction. Acetic acid, on reduction with lithium aluminium hydride, results in formation of ethanal, which on further reduction gives ethanol.

Trending Articles & Blogs
- Physics Tutor, Math Tutor Improve Your Child’s Knowledge
- How to Get Maximum Marks in Examination Preparation Strategy by Dr. Mukesh Shrimali
- 5 Important Tips To Personal Development Apply In Your Daily Life
- Breaking the Barriers Between High School and Higher Education
- 14 Vocational courses after class 12th
- Tips to Get Maximum Marks in Physics Examination
- Get Full Marks in Biology Class 12 CBSE
Download Old Sample Papers For Class X & XII
Download Practical Solutions of Chemistry and Physics for Class 12 with Solutions
Recent Questions Asked
- Newton’s laws of motion asked by Dr. Mukesh Shrimali
- Process of nutrition in Amoeba asked by Rajiv Sharma
- Importance of studying physics subject in school after 10th asked by Rajiv
- Refraction Through Prism in Different Medium asked by Kirti Sharma
- Ratio and Proportion Question asked by Education Desk
- Explain all the 12 tenses with example asked by Qwerty
- Refraction Through Prism in Different Medium asked by Seema Shrimali