Chapter : 4. Acid Bases & Salts
General Properties of Bases
General Properties of Bases :
1. The solutions of bases in water give a soapy touch. When dissolved in water they produce hydroxide ions (OH–) in solution.|
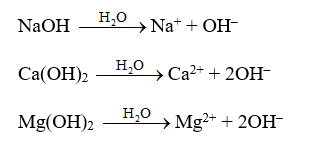
2. They turn red litmus paper blue.
Take some soap solution in a test tube. Dip the tip of a red litmus paper into it. You will see that red litmus paper turns blue. This indicates that the soap solution contains a base.
3. They react with acids to produce salt and water.
NaOH + HCI → NaCl + H2O
2KOH + H2SO4 → CuSO4 + 2H2O
Cu(OH)2 + H2SO4 → CuSO4 + 2H2O
In these reactions, the acid and the base neutralize each other. Therefore, these reactions are called neutralization reactions.
Thus, a neutralization reaction may be defined as a reaction between an acid and a base, producing salt and water.
This neutralization reaction may be explained as follows. You know, all acids provide H+ ions and all bases provide OH– ions in aqueous solution. Let us see what happens when HCl and NaOH react together. -
HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O
or H+ + Cl– + Na+ + OH– → Na+ + Cl– + H2O
or H+ + OH– → H2O
Thus, during neutralization of an acid with a base or vice versa H+ ions (from acid) and (OH–) ions (from base) combine to produce H2O molecules.
4. The oxides which produce acids in aqueous solutions are called acidic oxides which are usually the oxides of nonmetals. Acidic oxides react with bases to give salts and water.

5. When a base is heated with an ammonium salt, ammonia gas, another salt and water are produced. For example, when sodium hydroxide is heated with ammonium chloride, the products formed are sodium chloride, water and ammonia gas.
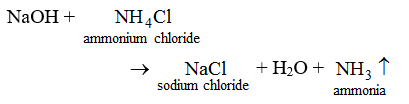
Ammonia gas is recognized by its pungent smell.
6. Bases react with certain salts to produce another salt and another base. For example, when NH4OH is added to a solution of Al2(SO4)3, (NH4)2SO4 and Al(OH)3 are produced.

1. The solutions of bases in water give a soapy touch. When dissolved in water they produce hydroxide ions (OH–) in solution.|
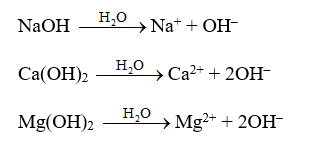
2. They turn red litmus paper blue.
Take some soap solution in a test tube. Dip the tip of a red litmus paper into it. You will see that red litmus paper turns blue. This indicates that the soap solution contains a base.
3. They react with acids to produce salt and water.
NaOH + HCI → NaCl + H2O
2KOH + H2SO4 → CuSO4 + 2H2O
Cu(OH)2 + H2SO4 → CuSO4 + 2H2O
In these reactions, the acid and the base neutralize each other. Therefore, these reactions are called neutralization reactions.
Thus, a neutralization reaction may be defined as a reaction between an acid and a base, producing salt and water.
This neutralization reaction may be explained as follows. You know, all acids provide H+ ions and all bases provide OH– ions in aqueous solution. Let us see what happens when HCl and NaOH react together. -
HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O
or H+ + Cl– + Na+ + OH– → Na+ + Cl– + H2O
or H+ + OH– → H2O
Thus, during neutralization of an acid with a base or vice versa H+ ions (from acid) and (OH–) ions (from base) combine to produce H2O molecules.
4. The oxides which produce acids in aqueous solutions are called acidic oxides which are usually the oxides of nonmetals. Acidic oxides react with bases to give salts and water.

5. When a base is heated with an ammonium salt, ammonia gas, another salt and water are produced. For example, when sodium hydroxide is heated with ammonium chloride, the products formed are sodium chloride, water and ammonia gas.
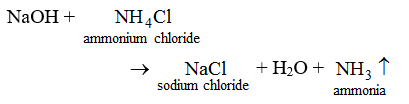
Ammonia gas is recognized by its pungent smell.
6. Bases react with certain salts to produce another salt and another base. For example, when NH4OH is added to a solution of Al2(SO4)3, (NH4)2SO4 and Al(OH)3 are produced.

Trending Articles & Blogs
- Physics Tutor, Math Tutor Improve Your Child’s Knowledge
- How to Get Maximum Marks in Examination Preparation Strategy by Dr. Mukesh Shrimali
- 5 Important Tips To Personal Development Apply In Your Daily Life
- Breaking the Barriers Between High School and Higher Education
- 14 Vocational courses after class 12th
- Tips to Get Maximum Marks in Physics Examination
- Get Full Marks in Biology Class 12 CBSE
Download Old Sample Papers For Class X & XII
Download Practical Solutions of Chemistry and Physics for Class 12 with Solutions
Recent Questions Asked
- Newton’s laws of motion asked by Dr. Mukesh Shrimali
- Process of nutrition in Amoeba asked by Rajiv Sharma
- Importance of studying physics subject in school after 10th asked by Rajiv
- Refraction Through Prism in Different Medium asked by Kirti Sharma
- Ratio and Proportion Question asked by Education Desk
- Explain all the 12 tenses with example asked by Qwerty
- Refraction Through Prism in Different Medium asked by Seema Shrimali