Chapter : 3. Work and Energy
Examples of Kinetic Energy
Example : 12
A bullet of mass 100 gm is fired with a velocity 50 m/s from a gun. Calculate the kinetic energy of the bullet.
Solution. Kinetic energy is given by
K.E. =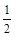 mv2
mv2
Here m = 100 gm = 0.1 kg; v = 500 m/s
K.E. =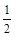 × 0.1 × (50)2
× 0.1 × (50)2
=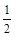 × 0.1 × 50 × 50 = 125 J
× 0.1 × 50 × 50 = 125 J
Example : 13
A 4 kg body is dropped from the top of a building of height 2.5 m. With what velocity will it strike the ground ? What is its kinetic energy when it strikes the ground ?
(Takes g = 9.8 m/s2)
Solution. Velocity of the body with which it strikes the ground can be calculated by using the equation, v2 = u2 + 2gh
Here, u = 0; g = 9.8 m/s2 ; h = 2.5 m
Substituting these values, we get
v2 = 02 + 2 × 9.8 × 2.5 = 49
or v = 7 m/s
Thus, the speed of the body with which it strikes the ground = 7 m/s.
Example : 14
Calculate the velocity of 4 kg mass with kinetic energy of 128 J.
Solution. The formula for kinetic energy is given by
K.E. =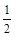 mv2
mv2
Here K.E. = 128 J; m = 4 kg
∴ 128 =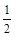 × 4 × v2
× 4 × v2
or v2 = 64; or v = 8 m/s
Example : 15
Which would have a greater effect on the kinetic energy of an object, doubling the mass or doubling the velocity ?
Solution. (i) The kinetic energy of a body is directly proportional to its "mass" (m). So, if we double the mass (so that it becomes 2m), then the kinetic energy will also get doubled.
(ii) On the other hand, kinetic energy of a body is directly proportional to the "square of its velocity" (v2). So, if we double the velocity (so that it becomes 2v), then the kinetic energy will become four times. This is because : (2v)2 = 4v2.
It is clear from the above discussion that doubling the velocity has a greater effect on the kinetic energy of an object.
A bullet of mass 100 gm is fired with a velocity 50 m/s from a gun. Calculate the kinetic energy of the bullet.
Solution. Kinetic energy is given by
K.E. =
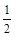 mv2
mv2Here m = 100 gm = 0.1 kg; v = 500 m/s
K.E. =
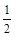 × 0.1 × (50)2
× 0.1 × (50)2 =
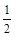 × 0.1 × 50 × 50 = 125 J
× 0.1 × 50 × 50 = 125 JExample : 13
A 4 kg body is dropped from the top of a building of height 2.5 m. With what velocity will it strike the ground ? What is its kinetic energy when it strikes the ground ?
(Takes g = 9.8 m/s2)
Solution. Velocity of the body with which it strikes the ground can be calculated by using the equation, v2 = u2 + 2gh
Here, u = 0; g = 9.8 m/s2 ; h = 2.5 m
Substituting these values, we get
v2 = 02 + 2 × 9.8 × 2.5 = 49
or v = 7 m/s
Thus, the speed of the body with which it strikes the ground = 7 m/s.
Example : 14
Calculate the velocity of 4 kg mass with kinetic energy of 128 J.
Solution. The formula for kinetic energy is given by
K.E. =
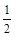 mv2
mv2 Here K.E. = 128 J; m = 4 kg
∴ 128 =
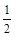 × 4 × v2
× 4 × v2or v2 = 64; or v = 8 m/s
Example : 15
Which would have a greater effect on the kinetic energy of an object, doubling the mass or doubling the velocity ?
Solution. (i) The kinetic energy of a body is directly proportional to its "mass" (m). So, if we double the mass (so that it becomes 2m), then the kinetic energy will also get doubled.
(ii) On the other hand, kinetic energy of a body is directly proportional to the "square of its velocity" (v2). So, if we double the velocity (so that it becomes 2v), then the kinetic energy will become four times. This is because : (2v)2 = 4v2.
It is clear from the above discussion that doubling the velocity has a greater effect on the kinetic energy of an object.
Trending Articles & Blogs
- Physics Tutor, Math Tutor Improve Your Child’s Knowledge
- How to Get Maximum Marks in Examination Preparation Strategy by Dr. Mukesh Shrimali
- 5 Important Tips To Personal Development Apply In Your Daily Life
- Breaking the Barriers Between High School and Higher Education
- 14 Vocational courses after class 12th
- Tips to Get Maximum Marks in Physics Examination
- Get Full Marks in Biology Class 12 CBSE
Download Old Sample Papers For Class X & XII
Download Practical Solutions of Chemistry and Physics for Class 12 with Solutions
Recent Questions Asked
- Newton’s laws of motion asked by Dr. Mukesh Shrimali
- Process of nutrition in Amoeba asked by Rajiv Sharma
- Importance of studying physics subject in school after 10th asked by Rajiv
- Refraction Through Prism in Different Medium asked by Kirti Sharma
- Ratio and Proportion Question asked by Education Desk
- Explain all the 12 tenses with example asked by Qwerty
- Refraction Through Prism in Different Medium asked by Seema Shrimali