Chapter : 3. Work and Energy
Inter conversion of potential And kinetic energy
Mechanical Energy of a Freely Falling Body :
Assume, a body of mass m is at rest at a height h from the earth's surface, as it starts falling, its velocity after travelling a distance x (point B) becomes v and its velocity on the earth's surface is v'.
Mechanical energy of the body at point A :
EA = Kinetic energy + Potential energy
EA = m(0)2 + mgh
EA = mgh ………(i)
Mechanical energy of the body at point B :
EB =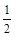 mv2 + mg (h – x) ……. ..(ii)
mv2 + mg (h – x) ……. ..(ii)

Mechanical energy of the body at point C :
EC =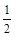 m (v')2 + mg × 0
m (v')2 + mg × 0
EC =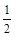 m (v')2 ……..(iv)
m (v')2 ……..(iv)
Use : EA = EB = EC
Hence, when a body falls freely, its mechanical energy will be constant. That means, the total energy of the body during free fall, remains constant at all positions. However, the form of energy keeps on changing at all points during the motion.
Assume, a body of mass m is at rest at a height h from the earth's surface, as it starts falling, its velocity after travelling a distance x (point B) becomes v and its velocity on the earth's surface is v'.
Mechanical energy of the body at point A :
EA = Kinetic energy + Potential energy
EA = m(0)2 + mgh
EA = mgh ………(i)
Mechanical energy of the body at point B :
EB =
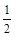 mv2 + mg (h – x) ……. ..(ii)
mv2 + mg (h – x) ……. ..(ii) 
Mechanical energy of the body at point C :
EC =
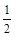 m (v')2 + mg × 0
m (v')2 + mg × 0EC =
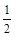 m (v')2 ……..(iv)
m (v')2 ……..(iv)Use : EA = EB = EC
Hence, when a body falls freely, its mechanical energy will be constant. That means, the total energy of the body during free fall, remains constant at all positions. However, the form of energy keeps on changing at all points during the motion.
Trending Articles & Blogs
- Physics Tutor, Math Tutor Improve Your Child’s Knowledge
- How to Get Maximum Marks in Examination Preparation Strategy by Dr. Mukesh Shrimali
- 5 Important Tips To Personal Development Apply In Your Daily Life
- Breaking the Barriers Between High School and Higher Education
- 14 Vocational courses after class 12th
- Tips to Get Maximum Marks in Physics Examination
- Get Full Marks in Biology Class 12 CBSE
Download Old Sample Papers For Class X & XII
Download Practical Solutions of Chemistry and Physics for Class 12 with Solutions
Recent Questions Asked
- Newton’s laws of motion asked by Dr. Mukesh Shrimali
- Process of nutrition in Amoeba asked by Rajiv Sharma
- Importance of studying physics subject in school after 10th asked by Rajiv
- Refraction Through Prism in Different Medium asked by Kirti Sharma
- Ratio and Proportion Question asked by Education Desk
- Explain all the 12 tenses with example asked by Qwerty
- Refraction Through Prism in Different Medium asked by Seema Shrimali