Chapter : 1. Metals & Non Metals
Extraction fo ron from Haematite
Extraction fo ron from Haematite :
1. Dressing of the ore :
The big lumps of the ore are broken into small pieces and then washed with water to remove clay, sand and other adhering impurities. The ore thus becomes ready for treatment in the blast furnace.
2. Smelting in the blast furnace :
The concentrated ore is mixed with coke and limestone. The mixture is charged at the top of a blast furnace. The following reactions occur in the furnace.
(i) As the charge comes down to the 873 K region, the iron oxide is reduced by the ascending carbon monoxide gas produced by the burning of coke.
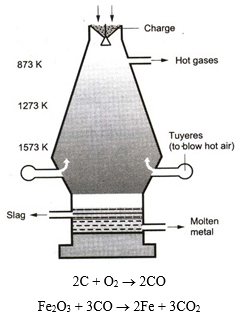
The iron thus obtained is called sponge iron.
(ii) At the 1273 K region, the silica is converted to slag.
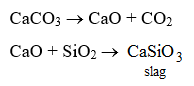
(iii) At the 1573 K region, sponge iron melts and dissolves carbon, phosphorus, silica, etc. The slag also fuses. The molten mass collects at the base of the furnace. The slag floats over it. The molten iron is taken out as required. This iron is called pig iron.
Function of limestone : Limestone is decomposed to give quicklime.
CaCO3 → CaO + CO2
Quicklime combines with impurities like sand to form a molten slag (calcium silicate).
CaO + SiO2 → CaSiO3
The slag floats on the surface of molten iron. It is taken out through a hole from time to time.
The formation of calcium silicate as slag not only removes unwanted silica but also keeps iron away from being oxidized.
1. Dressing of the ore :
The big lumps of the ore are broken into small pieces and then washed with water to remove clay, sand and other adhering impurities. The ore thus becomes ready for treatment in the blast furnace.
2. Smelting in the blast furnace :
The concentrated ore is mixed with coke and limestone. The mixture is charged at the top of a blast furnace. The following reactions occur in the furnace.
(i) As the charge comes down to the 873 K region, the iron oxide is reduced by the ascending carbon monoxide gas produced by the burning of coke.

The iron thus obtained is called sponge iron.
(ii) At the 1273 K region, the silica is converted to slag.
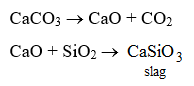
(iii) At the 1573 K region, sponge iron melts and dissolves carbon, phosphorus, silica, etc. The slag also fuses. The molten mass collects at the base of the furnace. The slag floats over it. The molten iron is taken out as required. This iron is called pig iron.
Function of limestone : Limestone is decomposed to give quicklime.
CaCO3 → CaO + CO2
Quicklime combines with impurities like sand to form a molten slag (calcium silicate).
CaO + SiO2 → CaSiO3
The slag floats on the surface of molten iron. It is taken out through a hole from time to time.
The formation of calcium silicate as slag not only removes unwanted silica but also keeps iron away from being oxidized.
Trending Articles & Blogs
- Physics Tutor, Math Tutor Improve Your Child’s Knowledge
- How to Get Maximum Marks in Examination Preparation Strategy by Dr. Mukesh Shrimali
- 5 Important Tips To Personal Development Apply In Your Daily Life
- Breaking the Barriers Between High School and Higher Education
- 14 Vocational courses after class 12th
- Tips to Get Maximum Marks in Physics Examination
- Get Full Marks in Biology Class 12 CBSE
Download Old Sample Papers For Class X & XII
Download Practical Solutions of Chemistry and Physics for Class 12 with Solutions
Recent Questions Asked
- Newton’s laws of motion asked by Dr. Mukesh Shrimali
- Process of nutrition in Amoeba asked by Rajiv Sharma
- Importance of studying physics subject in school after 10th asked by Rajiv
- Refraction Through Prism in Different Medium asked by Kirti Sharma
- Ratio and Proportion Question asked by Education Desk
- Explain all the 12 tenses with example asked by Qwerty
- Refraction Through Prism in Different Medium asked by Seema Shrimali