Chapter : 3. Atoms & Molecules
Relationship between mole, number of particles and mass and interconversion of one into the other
Relationship between mole, number of particles and mass and interconversion of one into the other.

Molarity (M) : - Moles of solute is one litre of solution is known as molarity.

Example. An ornament of silver contains 20 g of silver. Calculate the moles of silver present (atomic mass of silver = 180 u)
Solution. Moles of silver,

Mass of silver, m = 20 g,
Molar mass of silver,
M = 108 g
∴ n =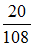 = 0.185 mol.
= 0.185 mol.
Example. How many moles of CO2 are present in 51.2 g of it ?
Solution. Molecular mass of CO2 = 12 + 2 + 16 = 44 u
Molar mass of CO2 (M) = 44 g
Mass of CO2 (m) = 51.2 g
Moles of CO2,

Example. Calculate the mass of
(i) 0.5 moles of N2 gas
(ii) 0.5 moles of N atoms
Solution. (i) 0.5 moles of N2 gas
Mass = Molar mass × Number of moles
m = M × n
M = 28 g, n = 0.5
m = 28 × 0.5 = 14 g
(ii) Mass = Molar mass × Number of moles
m = M × n
n = 0.5 mole, M = 14 g
m = 14 × 0.5 = 7 g

Molarity (M) : - Moles of solute is one litre of solution is known as molarity.

Example. An ornament of silver contains 20 g of silver. Calculate the moles of silver present (atomic mass of silver = 180 u)
Solution. Moles of silver,

Mass of silver, m = 20 g,
Molar mass of silver,
M = 108 g
∴ n =
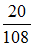 = 0.185 mol.
= 0.185 mol. Example. How many moles of CO2 are present in 51.2 g of it ?
Solution. Molecular mass of CO2 = 12 + 2 + 16 = 44 u
Molar mass of CO2 (M) = 44 g
Mass of CO2 (m) = 51.2 g
Moles of CO2,

Example. Calculate the mass of
(i) 0.5 moles of N2 gas
(ii) 0.5 moles of N atoms
Solution. (i) 0.5 moles of N2 gas
Mass = Molar mass × Number of moles
m = M × n
M = 28 g, n = 0.5
m = 28 × 0.5 = 14 g
(ii) Mass = Molar mass × Number of moles
m = M × n
n = 0.5 mole, M = 14 g
m = 14 × 0.5 = 7 g
Trending Articles & Blogs
- Physics Tutor, Math Tutor Improve Your Child’s Knowledge
- How to Get Maximum Marks in Examination Preparation Strategy by Dr. Mukesh Shrimali
- 5 Important Tips To Personal Development Apply In Your Daily Life
- Breaking the Barriers Between High School and Higher Education
- 14 Vocational courses after class 12th
- Tips to Get Maximum Marks in Physics Examination
- Get Full Marks in Biology Class 12 CBSE
Download Old Sample Papers For Class X & XII
Download Practical Solutions of Chemistry and Physics for Class 12 with Solutions
Recent Questions Asked
- Newton’s laws of motion asked by Dr. Mukesh Shrimali
- Process of nutrition in Amoeba asked by Rajiv Sharma
- Importance of studying physics subject in school after 10th asked by Rajiv
- Refraction Through Prism in Different Medium asked by Kirti Sharma
- Ratio and Proportion Question asked by Education Desk
- Explain all the 12 tenses with example asked by Qwerty
- Refraction Through Prism in Different Medium asked by Seema Shrimali