Chapter : Motion in one Dimension
Comparative Study of Instantaneous Speed and Instantaneous Velocity
Comparative Study of Instantaneous Speed and Instantaneous Velocity
Instantaneous velocity or simply velocity is defined as rate of change of particle's position with time =
=  where the position
where the position 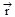 of a particle at any instant changes by Δ
of a particle at any instant changes by Δ 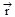 in a small time Δ t. he magnitude of velocity is called speed i.e. speed = | velocity | i.e. v = |
in a small time Δ t. he magnitude of velocity is called speed i.e. speed = | velocity | i.e. v = |  |
|
Note : In straight line motion there is no change in direction so and v both have same meaning.
and v both have same meaning.
Note :
(a) Velocity is a vector while speed is a scalar having same units (m/s) and dimension [LT–1]
(b) If during motion velocity remains constant throughout a given interval of time, the motion is said to be uniform and for uniform motion, = constant =
= constant = 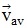
However converse may or may not be true i.e. If =
= 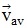 , the motion may or may not be uniform.
, the motion may or may not be uniform.
(c) If velocity is constant, speed ( = | velocity |) will also be constant. However conversdree may or may not be true i.e. if speed = constant, velocity may or may not be constant as velocity has a direction in addition to magnitude which may or may not change. e.g. in case of uniform rectilinear motion. = constant and so speed |
= constant and so speed | | = constant while in case of uniform circular motion, v = constant but
| = constant while in case of uniform circular motion, v = constant but  ≠ constant due to change in direction.
≠ constant due to change in direction.
(d) Velocity can be positive or negative, as it is a vector but speed can never be negative as it is the magnitude of velocity i.e. v = | |
|
(e) If displacement is given as a function of time, the time derivative of displacement will give velocity and modulus of velocity gives speed.
e.g. s = A0 – A1t + A2t2, v = = – A1 + 2A2t. So, initially (t = 0), velocity = – A1, while speed = |–A1| = A1
= – A1 + 2A2t. So, initially (t = 0), velocity = – A1, while speed = |–A1| = A1
Special Note : It is common misconception, that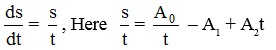 Which is totally different from the above value of
Which is totally different from the above value of  .
.
(f) As by definition, v = , the slope of displacement versus time graph gives velocity.
, the slope of displacement versus time graph gives velocity.
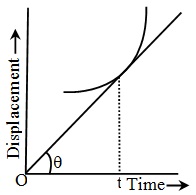
i.e. v = = tan θ = slope of s-t curve
= tan θ = slope of s-t curve
(g) As, v = ⇒ ds = vdt
⇒ ds = vdt
From figure vdt = dA. so, dA = ds
∴
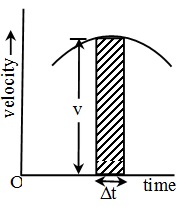
Area under velocity versus time graph with proper algebraic sign gives displacement while without sign gives distance.
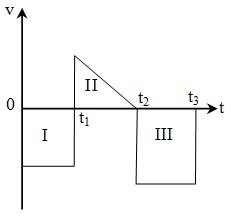
e.g. From the adjoining v-t graph.
The distance travelled by body in time t3 = Area I + Area II + Area III and the displacement of body = Area II – Area III – Area I
Instantaneous velocity or simply velocity is defined as rate of change of particle's position with time
 =
=  where the position
where the position 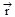 of a particle at any instant changes by Δ
of a particle at any instant changes by Δ 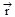 in a small time Δ t. he magnitude of velocity is called speed i.e. speed = | velocity | i.e. v = |
in a small time Δ t. he magnitude of velocity is called speed i.e. speed = | velocity | i.e. v = |  |
| Note : In straight line motion there is no change in direction so
 and v both have same meaning.
and v both have same meaning.Note :
(a) Velocity is a vector while speed is a scalar having same units (m/s) and dimension [LT–1]
(b) If during motion velocity remains constant throughout a given interval of time, the motion is said to be uniform and for uniform motion,
 = constant =
= constant = 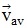
However converse may or may not be true i.e. If
 =
= 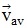 , the motion may or may not be uniform.
, the motion may or may not be uniform.(c) If velocity is constant, speed ( = | velocity |) will also be constant. However conversdree may or may not be true i.e. if speed = constant, velocity may or may not be constant as velocity has a direction in addition to magnitude which may or may not change. e.g. in case of uniform rectilinear motion.
 = constant and so speed |
= constant and so speed | | = constant while in case of uniform circular motion, v = constant but
| = constant while in case of uniform circular motion, v = constant but  ≠ constant due to change in direction.
≠ constant due to change in direction.(d) Velocity can be positive or negative, as it is a vector but speed can never be negative as it is the magnitude of velocity i.e. v = |
 |
|(e) If displacement is given as a function of time, the time derivative of displacement will give velocity and modulus of velocity gives speed.
e.g. s = A0 – A1t + A2t2, v =
 = – A1 + 2A2t. So, initially (t = 0), velocity = – A1, while speed = |–A1| = A1
= – A1 + 2A2t. So, initially (t = 0), velocity = – A1, while speed = |–A1| = A1 Special Note : It is common misconception, that
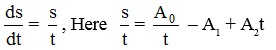 Which is totally different from the above value of
Which is totally different from the above value of  .
.(f) As by definition, v =
 , the slope of displacement versus time graph gives velocity.
, the slope of displacement versus time graph gives velocity. 
i.e. v =
 = tan θ = slope of s-t curve
= tan θ = slope of s-t curve(g) As, v =
 ⇒ ds = vdt
⇒ ds = vdt From figure vdt = dA. so, dA = ds
∴


Area under velocity versus time graph with proper algebraic sign gives displacement while without sign gives distance.

e.g. From the adjoining v-t graph.
The distance travelled by body in time t3 = Area I + Area II + Area III and the displacement of body = Area II – Area III – Area I
Trending Articles & Blogs
- Physics Tutor, Math Tutor Improve Your Child’s Knowledge
- How to Get Maximum Marks in Examination Preparation Strategy by Dr. Mukesh Shrimali
- 5 Important Tips To Personal Development Apply In Your Daily Life
- Breaking the Barriers Between High School and Higher Education
- 14 Vocational courses after class 12th
- Tips to Get Maximum Marks in Physics Examination
- Get Full Marks in Biology Class 12 CBSE
Download Old Sample Papers For Class X & XII
Download Practical Solutions of Chemistry and Physics for Class 12 with Solutions