Chapter : Newton's Laws Of Motion & Friction
Points to Remember - Newton's Laws Of Motion & Friction
POINTS TO REMEMBER 1. Newton's Ist Law of motion states that every body has tendency to oppose any change in its state of motion. This property of objects is called Inertia.
2. Inertia is of three types (i) Inertia of rest (ii) Inertia of motion and (iii) Inertia of direction.
3. Inertia ∝ mass.
4. Linear momentum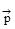 = m
= m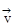
5. Newton's IIndlaw of motion states that rate of change of momentum is equal to applied force.
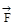 =
= 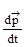 = m
= m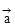
1 Newton = 105dyne
6. Newton's Istand IIIrdlaw can be derived from second law therefore IIndlaw is the most fundamental law out of the three law.
7. Impulse =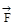 Δt = Δ
Δt = Δ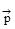 =
= 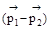
8. According to law of conservation of linear momentum :
Initial Momentum = Final Momentum
m1u1+ m2u2 = m1v1+ m2v2
9. Thrust on rocket
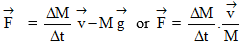
according as gravity is present or absent.
10. Acceleration of rocket
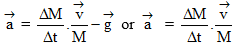
according as gravity is present or absent.
11. For equilibrium of a body under the action of concurrent forces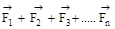 = 0
= 0
12. Apparent weight of a body in the lift accelerated up is W = m (g + a).
13. Apparent weight of a body in the lift accelerated down is W = m (g – a)
14. If the downward acceleration of the lift is a = g, then W = 0 i.e. the body will enjoy weightlessness.
15. If the downward acceleration of the body is a > g, then W is negative, the body will rise up to the ceiling of lift.
2. Inertia is of three types (i) Inertia of rest (ii) Inertia of motion and (iii) Inertia of direction.
3. Inertia ∝ mass.
4. Linear momentum
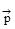 = m
= m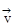
5. Newton's IIndlaw of motion states that rate of change of momentum is equal to applied force.
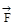 =
= 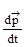 = m
= m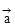
1 Newton = 105dyne
6. Newton's Istand IIIrdlaw can be derived from second law therefore IIndlaw is the most fundamental law out of the three law.
7. Impulse =
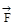 Δt = Δ
Δt = Δ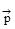 =
= 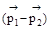
8. According to law of conservation of linear momentum :
Initial Momentum = Final Momentum
m1u1+ m2u2 = m1v1+ m2v2
9. Thrust on rocket
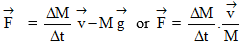
according as gravity is present or absent.
10. Acceleration of rocket
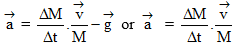
according as gravity is present or absent.
11. For equilibrium of a body under the action of concurrent forces
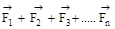 = 0
= 0 12. Apparent weight of a body in the lift accelerated up is W = m (g + a).
13. Apparent weight of a body in the lift accelerated down is W = m (g – a)
14. If the downward acceleration of the lift is a = g, then W = 0 i.e. the body will enjoy weightlessness.
15. If the downward acceleration of the body is a > g, then W is negative, the body will rise up to the ceiling of lift.
Trending Articles & Blogs
- Physics Tutor, Math Tutor Improve Your Child’s Knowledge
- How to Get Maximum Marks in Examination Preparation Strategy by Dr. Mukesh Shrimali
- 5 Important Tips To Personal Development Apply In Your Daily Life
- Breaking the Barriers Between High School and Higher Education
- 14 Vocational courses after class 12th
- Tips to Get Maximum Marks in Physics Examination
- Get Full Marks in Biology Class 12 CBSE
Download Old Sample Papers For Class X & XII
Download Practical Solutions of Chemistry and Physics for Class 12 with Solutions